Why Bitcoin? A Simple Guide for Curious Beginners
If you’re like most people, the idea of Bitcoin probably feels overwhelming. Maybe it sounds like tech jargon or risky internet money. But what if I told you Bitcoin is much simpler than you think? To understand it, we need to start by asking one basic question:

What Is Money, Really?
Money isn’t just paper bills or numbers in a bank app. It’s a tool. Humans created money to store value, exchange it, and measure it. Throughout history, we’ve used many things as money: shells, salt, gold, silver, and eventually government-issued paper.
In 1971, something big changed. Governments stopped backing money with gold. Since then, most countries have used fiat money, which holds value only because the government declares it does. Central banks now have the power to create unlimited amounts of this money, which often results in inflation.
Inflation causes your dollars to lose purchasing power over time. Prices go up, and your savings buy less. On top of that, the money in your bank account is not completely under your control. The bank legally owns it and can freeze or limit your access. This entire setup relies on centralized institutions that are not directly accountable to you.
Bitcoin: A Different Kind of Money
Bitcoin didn’t just appear out of nowhere. It was born in 2009, right after a global financial crisis exposed the fragility of the banking system and the dangers of unchecked money printing. Its anonymous creator, known as Satoshi Nakamoto, wasn’t just building software. They were making a statement.
Bitcoin was created in direct response to the problems of fiat money.Money that can be created endlessly, loses purchasing power over time, and is controlled by central authorities. It asks a bold and uncomfortable question:
What is money really worth if it can be printed without limit, steadily loses value, and is never truly yours to control?
For decades, people had no real alternative. Fiat currencies dominate the global economy. Most of us hold our savings in government-issued money, stored in banks that we don’t control, governed by policies we don’t vote on, and manipulated by forces we don’t fully understand.
Bitcoin changes that. It presents a new kind of money that is designed for the internet age and built from first principles. It doesn’t require trust in banks or governments. It doesn’t depend on central planners or inflation targets. Instead, it runs on mathematics, computer code, and open-source collaboration.
What Makes Bitcoin Fundamentally Different
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Fixed Supply | Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist. This rule is built into the code and enforced by the network. |
| Permissionless Access | Anyone with internet access can use Bitcoin. No bank account or approval is needed. |
| True Ownership | You control your Bitcoin directly with your cryptographic keys. No one can take it from you. |
| Censorship Resistance | No government or company can block a transaction. Bitcoin operates globally, around the clock. |
| Transparency and Trust in Code | Every transaction is public, and every rule is open for anyone to verify. |
Bitcoin is not just an investment or a technology trend. At its core, it is a peaceful revolution, a voluntary opt-out from a system that many believe is failing. It brings us back to sound money, where scarcity matters, transparency is the norm, and individuals, not institutions, hold the power.

Bitcoin was created as a response to the problems of fiat money. It challenges the idea that value can come from endless printing, asking: What is money really worth if you don’t truly control it?
How Bitcoin Works (In Plain Language)
Imagine a massive notebook that exists on thousands of computers around the world. Every time someone sends Bitcoin, it gets recorded in this notebook. This is called the blockchain.
When Alice Sends Bitcoin to Bob
- Alice uses her private key, like a secret password, to sign the transaction.
- The transaction is broadcast to the global Bitcoin network for verification.
- Miners collect transactions and add them to a new page called a block.
- Miners solve a math puzzle through a process known as proof-of-work.
- The winning miner adds the block to the blockchain and earns new Bitcoin along with transaction fees.
- The transaction is finalized. Once added to the blockchain, it becomes permanent and secure.
There is no need to trust any person or institution. You only need to trust the math and the Bitcoin protocol.
Why Bitcoin Is Unique
Here are some of Bitcoin’s key traits:
| Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Scarcity | Only 21 million bitcoins will ever exist. This supply limit is coded in. |
| Decentralization | No central authority controls it. It runs on a global network. |
| Ownership | You hold your Bitcoin using cryptographic keys. You have full control. |
| Transparency | All transactions are public. Anyone can verify them. |
| Durability | Bitcoin exists on a resilient network of computers. |
| Portability | You can carry your wealth anywhere using just a password or hardware device. |
| Divisibility | One Bitcoin equals 100 million units, called Satoshis. |
| Censorship Resistance | No one can block or stop your transaction. |
Bitcoin’s Role in the History of Money
Bitcoin is moving through the same stages that traditional money has followed. It’s evolving just like gold and other forms of money did, gaining trust, usefulness, and eventually full monetary status.
- Collectible – New forms of money often begin as novelties or items valued by niche communities.
- Store of Value – As trust builds, it starts being used to preserve wealth over time.
- Medium of Exchange – With greater acceptance, it becomes practical for everyday purchases and transactions.
- Unit of Account – Eventually, prices may be set directly in the new form of money.
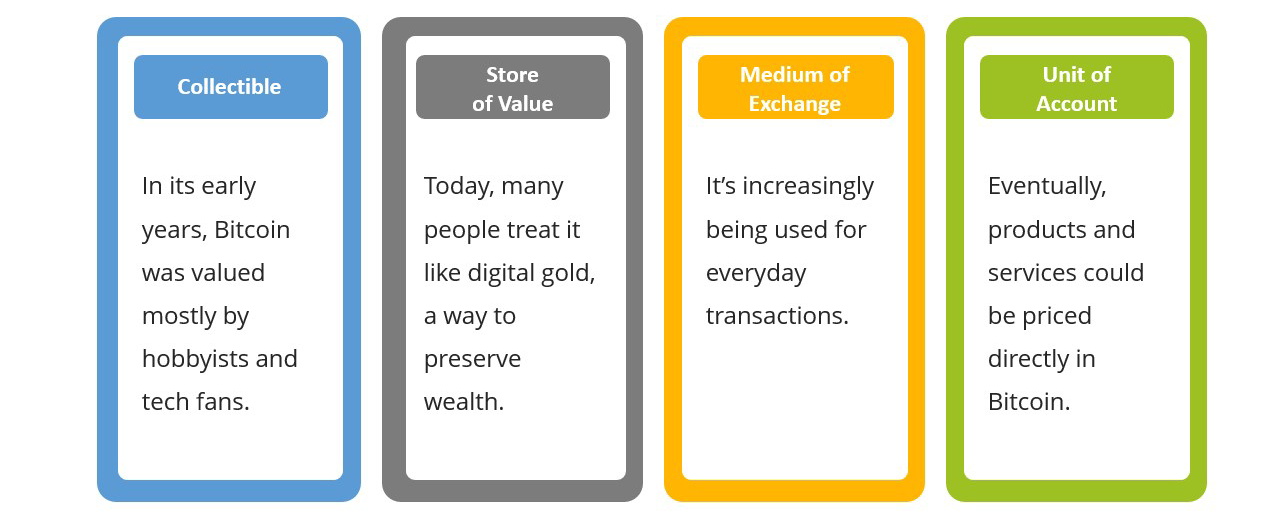
Bitcoin is following the classic path of sound money. This timeline shows how its role is evolving across four key stages.
What About the Common Questions?
Bitcoin Is About Choice and Freedom
Bitcoin offers something the current system does not. It gives people a way to opt out of inflation, control their own money, and build a future that doesn’t depend on trust in institutions.
You don’t need to buy a whole Bitcoin. Even a few Satoshis — a fraction of a Bitcoin — can matter. As Bitcoin continues to grow, even small amounts could have significant value.
From Scarcity Comes Abundance
That is the promise. That is the power.
That is Bitcoin.
